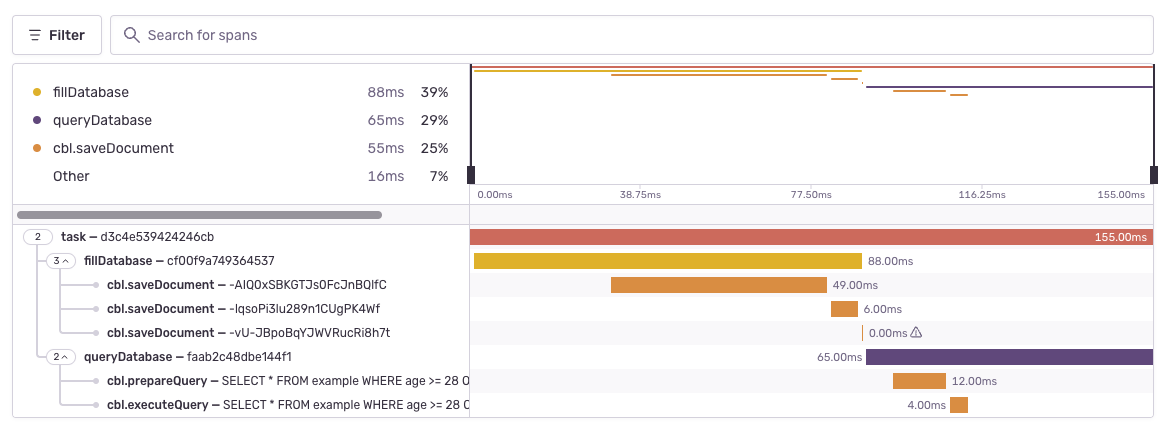
Instrumentation
The execution of certain operations can be traced through the tracing API. This is useful for debugging and performance profiling.
CBL Dart has builtin trace points at which flow control is given to the
currently installed TracingDelegate.
Included in this package is the DevToolsTracing delegate, which records
timeline events that can be later visualized through the Dart DevTools
Performance Page.
You can install a delegate by calling TracingDelegate.install:
await TracingDelegate.install(DevToolsTracing());
Sentry
The Sentry integration provided by cbl_sentry installs a
DevToolsTracing to transparently record breadcrumbs and transaction spans.
Features
- Record log messages as Sentry breadcrumbs
- Record CBL Dart API usage as Sentry breadcrumbs
- Record CBL Dart operations as Sentry transaction spans
Limitations
Sentry currently does not support binding transaction spans to zones. This means there can only be one global transaction span that integrations can transparently access. To support more advanced use cases, this package provides a mechanism to bind transaction spans to zones. This mechanism will be removed if and when Sentry supports this natively.
Getting started
-
Make sure your app is setup for using Couchbase Lite.
-
Add the
cbl_sentrypackage as a dependency:flutter pub add cbl_sentry -
Add the
CouchbaseLiteIntegrationwhen configuring Sentry:import 'package:cbl_sentry/cbl_sentry.dart';
import 'package:sentry/sentry.dart';
void main() {
Sentry.init(
(options) {
options
..dsn = ...
// While testing your Sentry configuration, make sure that all traces are sampled.
..tracesSampleRate = 1
// Add the CBL Dart integration.
..addIntegration(CouchbaseLiteIntegration());
},
appRunner: () async {
runApp(MyApp());
}
);
}To find out about configurable options, see the documentation of
CouchbaseLiteIntegration.cautionMake sure you don't install a
TracingDelegatewhen using theCouchbaseLiteIntegration. The integration has to be able to install aTracingDelegateitself.
Performance tracing
This integration only records transaction spans when a transaction has been started and a child span of the transaction is available in the environment.
To find a span, the integration uses cblSentrySpan. This is
a getter that returns either a span that has been bound to the current zone or
as a fallback the result of Sentry.getSpan. To bind a
span to a zone use runWithCblSentrySpan.
The following code snippet shows functions that are useful to trace the performance of operations in an app:
Future<T> runAppTransaction<T>(String name, Future<T> Function() fn) =>
_runAppSpan(Sentry.startTransaction(name, 'task'), fn);
Future<T> runAppOperation<T>(String name, Future<T> Function() fn) =>
_runAppSpan(cblSentrySpan!.startChild(name), fn);
Future<T> _runAppSpan<T>(ISentrySpan span,Future<T> Function() fn) async {
try {
return await runWithCblSentrySpan(span, fn);
// ignore: avoid_catches_without_on_clauses
} catch (e) {
span
..throwable = e
..status = const SpanStatus.internalError();
rethrow;
} finally {
span.status ??= const SpanStatus.ok();
await span.finish();
}
}
A app operation like the one below is traced as a transaction span, with CBL Dart operations as child spans:
Future<void> queryDatabase() => runAppOperation('queryDatabase', () async {
final query = await db.createQuery(
'SELECT * FROM example WHERE age >= 28 OR name LIKE "A%"',
);
final resultSet = await query.execute();
final results = await resultSet
.asStream()
.map((result) => result.toPlainMap())
.toList();
prettyPrintJson(results);
});